Chapter V – Roads, sandpits and forest infrastructures
Division II – Roads
§5. Maintenance and closure of a road
Section 81
The techniques used during the temporary or permanent closure of a road must prevent the obstruction of the water flow and the sedimentation in watercourses. They must also ensure the free flow of fish to the crossing site in situations other than those described in section 103.
They must also ensure the free flow of fish to the crossing site in situations other than those described in section 103. 
1
Objectives
- To preserve the integrity of an aquatic, wetland or riparian environment
- To avoid carrying sediment into an aquatic, wetland or riparian environment
2
Objectives
- To preserve the integrity of an aquatic, wetland or riparian environment
- To preserve the integrity of a wildlife habitat
- To ensure the free flow of fish
Explanations
Section 103 describes situations in which the free flow of fish need not be ensured when developing a culvert, because the watercourse presents one or more obstacles to the fish close to the site of the crossing. Situations other than those described in section 103 are therefore cases in which the free flow of fish must be ensured. The techniques used during the temporary or permanent closure of a road must allow for this objective to be achieved.
Additional information
Citizens, companies or organizations wishing to obtain the closure of a road on land in the domain of the State ![]() (in French only) may request either temporary or permanent closure.
(in French only) may request either temporary or permanent closure.
The procedure and form can be found in the guide ![]() (in French only) and form
(in French only) and form ![]() (in French only) for applications for closure of a multi-purpose road.
(in French only) for applications for closure of a multi-purpose road.
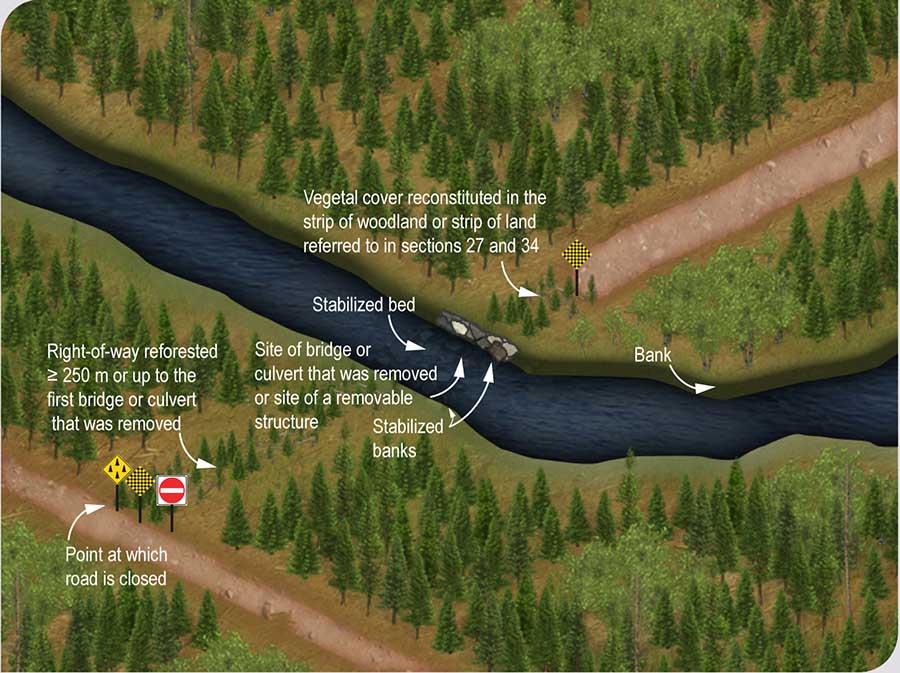
Where a road, closed permanently, has bridges, culverts or removable structures, they must be removed when the road is closed. After their removal, the bed and banks of the watercourses must be stabilized. The vegetal cover in the strip of woodland or the strip of land referred to in section 27 or 34 must be reconstituted.  The right-of-way of the road must be reforested over a minimum length of 250 m from the point of closure or up to the first bridge, culvert or removable structure removed in order to make use impossible. Reforestation must be carried out within 2 years using species adapted to the site.
The right-of-way of the road must be reforested over a minimum length of 250 m from the point of closure or up to the first bridge, culvert or removable structure removed in order to make use impossible. Reforestation must be carried out within 2 years using species adapted to the site.
3
Objectives
- To preserve the integrity of an aquatic, wetland or riparian environment
- To avoid carrying sediment into an aquatic, wetland or riparian environment
- To ensure the free flow of water
- To ensure the free flow of fish
- To make it impossible for the road to be used after closure
- To ensure that forest production is resumed on the site
Figure 81 Work to be carried out for permanent closure of a road
4
Objectives
- To make it impossible for the road to be used after closure
- To ensure that forest production is resumed on the site
Figure 81 Work to be carried out for permanent closure of a road
The renewal of the vegetation cover and reforestation of the right-of-way of the road, provided for in the second paragraph, do not apply to forest development activities carried out in the right-of-way of power transmission lines by the holder of a forestry permit issued for public utility works. 
5
Objective
- To obtain the operational flexibility required for certain forest development activities
Explanations
A person holding a forestry permit issued for public utility works is not required to renew the vegetation cover or carry out reforestation of the right-of-way of a road that has been permanently closed and is located in the right-of-way of power transmission lines.
Additional information
The Sustainable Forest Development Act ![]() states that a forestry permit is required to carry out certain forest development activities in forests in the domain of the State (section 73
states that a forestry permit is required to carry out certain forest development activities in forests in the domain of the State (section 73 ![]() ). The Act allows the Minister to issue a permit authorizing the holder to carry out the forest development activities specified on the permit, on the conditions determined by the Minister (section 74).
). The Act allows the Minister to issue a permit authorizing the holder to carry out the forest development activities specified on the permit, on the conditions determined by the Minister (section 74).